Azure Event Grid
Overview
Azure Event Grid is an eventing backplane that enables event-driven, reactive programming. It uses the publish-subscribe model.
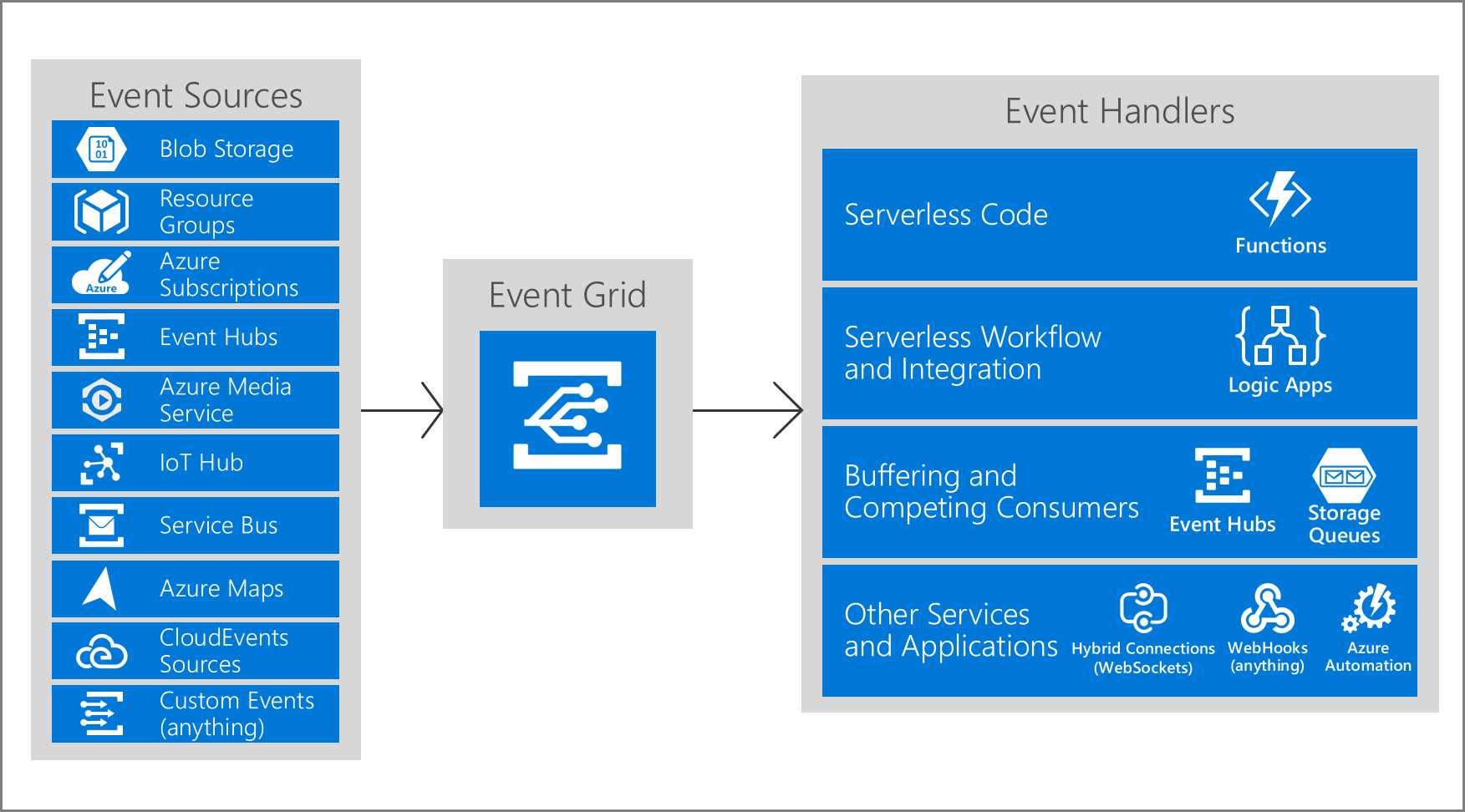
Azure Event Grid consists of:
- Events
- Event sources
- Topics
- Event subscriptions
- Event handlers
Topics
There are two categories of topics:
- System topics: built-in topics provided by Azure services. System topics are not visible in the Azure subscription because the publisher owns the topics, but it is possible to subscribe to it.
- Custom topics: application and third-party topics. When access to a custom topic is created or assigned, custom topic becomes visible in the Azure subscription.
Events
Events consists of four required string properties:
idsubjecteventTypeeventTime
An event of size up to 64 KB is covered by General Availability (GA) Service Level Agreement (SLA). The support for an event of size up to 1 MB is currently in preview. Events over 64 KB are charged in 64-KB increments.
Event sources send events to Azure Event Grid in an array, which can have several event objects. The array can have a total size of up to 1 MB. Each event in the array is limited to 1 MB. If an event of the array is greater then the size limits, response will be 413 Payload Too Large.
Subscribers use the subject to filter and route events. For example, path like /a/b/c in the subject can be filtered by the first segment /a to get a broad set of events like /a/b/c or /a/d/e.
CloudEvents Support
In addition to its default event schema, Azure Event Grid natively supports events in the JSON implementation of CloudEvents v1.0 and HTTP protocol binding. CloudEvents is an open specification for describing event data. It simplifies interoperability by providing a common event schema for publishing, and consuming cloud based events.
The header values for events delivered in the CloudEvents schema and the Event Grid schema are the same except for content-type. For cloudEvents schema, that header value is:
content-type: application/cloudevents+json; charset=utf-8
For Event Grid schema, that header value is:
content-type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Event Delivery Durability
Retry Schedule
When Event Grid receives an error for an event delivery attempt, Event Grid decides whether it should:
- retry the delivery,
- dead-letter the event,
- drop the event based on the type of the error.
These types of endpoints and errors for which retry doesn't happen:
| Endpoint Type | Error codes |
|---|---|
| Azure Resources | 400 Bad Request, 403 Forbidden, 413 Payload Too Large |
| Webhooks | 400 Bad Request, 401 Unauthorized, 403 Forbidden, 404 Not Found, 413 Payload Too Large |
Event Grid waits 30 seconds for a response when delivering a message. After 30 seconds the message is queued for a retry. Event Grid uses an exponential backoff retry policy for event delivery.
The following limits can be configured for the retry policy:
- Maximum number of attempts
- Event time-to-live (TTL)
Event Grid can be configured to batch events from delivery for improved HTTP performance in high-throughput scenarios. Batched delivery has two settings:
- Max events per batch: this number will never be exceeded, however fewer events may be delivered if no other events are available at the time of publish. Must be between
1and5,000. - Preferred batch size in KB: the batch size may be smaller if more events aren't available at the time of publish. It's possible that a batch is larger than the preferred batch size if a single event is larger than the preferred size.
Dead-letter Events
Event Grid can send undelivered event to a storage account. This process is known as dead-lettering.
Event Grid dead-letters an event when one of the following conditions is met:
- event isn't delivered within the time-to-live period,
- the number of tries to deliver the event exceeds the limit.
Adding Custom Headers
Event subscriptions allow to set up to 10 custom HTTP headers. Each header value shouldn't be greater then 4,096 (4KB) bytes. Custom headers on the events can be set for the following destinations:
- Webhooks
- Azure Service Bus topics and queues
- Azure Event Hubs
- Relay Hybrid Connections
Control Access to Events
Azure Event Grid allows to control the level of access given to different users to do various management operations. Even Grid uses Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC).
Event Grid provides the following built-in roles:
- Event Grid Subscription Reader: allows to read Event Grid event subscriptions.
- Event Grid Subscription Contributor: allows to manage Event Grid event subscription operations.
- Event Grid Contributor: allows to create and manage Event Grid resources.
- Event Grid Data Sender: allows to send event to Event Grid topics.
Permissions for Event Subscriptions
Event handler that isn't a WebHook requires write access to that resource. This permissions check prevents an unauthorized user from sending events to the resource.
Microsoft.EventGrid/EventSubscriptions/Write permission is required on the resource that is the event source in order to be able to subscribe to it. The required resource differs based on whether event subscription is for system topic or custom topic.
Format of the resource for system topics is:
/subscriptions/{subscription-id}/resourceGroups/{resource-group-name}/providers/{resource-provider}/{resource-type}/{resource-name}
Format of the resource for custom topics is:
/subscriptions/{subscription-id}/resourceGroups/{resource-group-name}/providers/Microsoft.EventGrid/topics/{topic-name}
Event Filtering
There are three filter options available when creating an event subscription:
- Event types
- Subject begins with or ends with
- Advanced fields and operators
Event type filtering example:
"filter": {
"includedEventTypes": [
"Microsoft.Resources.ResourceWriteFailure",
"Microsoft.Resources.ResourceWriteSuccess"
]
}
Subject filtering example:
"filter": {
"subjectBeginsWith": "/blobServices/default/containers/mycontainer/log",
"subjectEndsWith": ".jpg"
}
Advanced filtering example:
"filter": {
"advancedFilters": [
{
"operatorType": "NumberGreaterThanOrEquals",
"key": "Data.Key1",
"value": 5
},
{
"operatorType": "StringContains",
"key": "Subject",
"values": ["container1", "container2"]
}
]
}